Male Infertility
Dr. Kavoussi is the only physicians in Austin who are Specialty Fellowship trained in male infertility.
While most couples typically assume and seek diagnoses for female infertility, often a couple’s inability to conceive is linked to male infertility. We evaluate both male and female patients and when a male infertility diagnosis is made, we treat in-area Austin male infertility patients and patients from across the Unites States in either of our three specialty Austin Male Infertility offices. Along with Dr. Kavoussi’s clinical interest in male infertility, he has been involved in research to help advance the field. This includes scientific research investigating new methods on cellular levels to improve the success rate and efficiency in an animal model of sperm retrieval. This groundbreaking research will be applied ultimately to men with no sperm in their semen so they and their partners may undergo IVF with the man’s sperm with more efficiency and higher success rates.
Schedule a Private Consultation in our Austin Male Infertility office today! Call (512) 444-1414 or request an appointment online.
Click here for more information on comprehensive fertility care for the couple at Austin Fertility & Reproductive Medicine.
Frequently asked questions:
How common is male infertility?
 Infertility affects approximately 15% of couples trying to conceive. Around 20% of couples with infertility solely have a male factor as the cause. Another 30-40% of cases involve both male and female factor, so 50-60% of the time there is male factor involvement. While few clinics exist to address male infertility, we have 2 male infertility Texas area-location clinics to help local patients and patients traveling for treatment from abroad. All of our male infertility, TX offices are conveniently located in Austin and Round Rock, TX.
Infertility affects approximately 15% of couples trying to conceive. Around 20% of couples with infertility solely have a male factor as the cause. Another 30-40% of cases involve both male and female factor, so 50-60% of the time there is male factor involvement. While few clinics exist to address male infertility, we have 2 male infertility Texas area-location clinics to help local patients and patients traveling for treatment from abroad. All of our male infertility, TX offices are conveniently located in Austin and Round Rock, TX.
What is male infertility?
Male infertility is any condition that does not allow the production or delivery of fully functioning sperm with adequate numbers, ability swim, and normal shapes to his female partner adversely affecting their chances of achieving a pregnancy.
How is male infertility diagnosed?
Patients in our male infertility Austin offices have both a complete history and a physical examination performed with a focus on reproduction as a first step. This is followed by a semen analysis that will give information on the semen volume, number of sperm, how well the sperm can swim, and how many of the sperm have normal shapes. All of these parameters can be important for a man’s fertility potential. Depending on the findings of the semen analysis, a second semen analysis may be required as well as blood work examining the man’s hormones and possibly blood work for genetic testing may be needed.
What causes can affect a man’s fertility?
Causes for male factor infertility can include genetic (chromosome) disorders or hormonal (endocrine) issues which can affect the production and/or quality of sperm cells, having a history of an undescended testicle, having a varicocele (veins that are abnormally dilated around the testicle), having a history of testicular infection, having had radiation or chemotherapy treatments, smoking tobacco, drug use, specific medications, occupational exposures, toxins in the environment, excessive alcohol, anatomic duct blockages, ejaculation issues, and unknown causes.
Can cigarette smoke really affect a man’s fertility?
Absolutely. Smoking can affect the numbers of sperm and how well they swim. Smoking can also impact the seminal fluid which is ejaculated with the sperm.
Can anabolic steroids used for steroids have a bad impact on a man’s fertility?
Yes. Taking steroids can shut down a man’s natural production of hormones which are necessary for sperm production.
Is it common for a man to have no sperm present in the semen at all?
It is surprisingly common that 1 in 100 men (1%) have no sperm in the semen and 15% of men who seek medical care for infertility have no sperm in the semen.
Is there anything that can be done for couples to help them have a child using the man’s sperm and the woman’s egg when there is no sperm in the semen?
Yes. If there is no sperm in the semen due to an anatomic blockage (obstructive azoospermia) such as a vasectomy or a blockage where the tubes carrying the sperm enter the prostate gland, surgical reconstruction (vasectomy reversal), sperm retrieval, or unblocking the area can be offered. In men with no sperm in the semen without a blockage (non-obstructive azoospermia), a very specialized procedure called a microdissection testicular sperm extraction (microTESE) can be offered after genetic testing is performed to give us an understanding of what the odds will be to find sperm in each individual’s testicle. In men who are candidates for microTESE, it is possible to find small pockets of sperm production within the testicle under the visualization of an operative microscope, and this sperm can be retrieved and used in combination with IVF. The success rates of retrieving sperm using this procedure are highly dependent on the experience of the microsurgeon. Dr. Kavoussi is specialty fellowship trained in microsurgery to find such pockets of sperm production to allow these couples a chance to achieve a pregnancy with the man’s sperm.
What are the different types of sperm retrievals when it is due to an anatomic blockage?
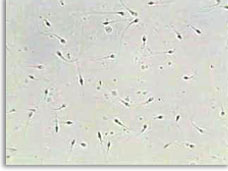
In those cases in which a man has a blockage (non-surgically correctable) that prevents the sperm to reach the semen, several options still exist for sperm retrieval that may be utilized in combination with assisted reproductive techniques (ART), including in vitro fertilization (IVF), to successfully achieve a pregnancy. Sperm retrieval may be accomplished via several options including percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration (PESA) where aspiration is performed from the epididymis (the anatomic structure connecting the testicle to the vas deferens), microsurgical epididymal sperm aspiration (MESA), testicular sperm aspiration (TESA) aspirating sperm directly from the testicle, and testicular sperm extraction (TESE).
What are our goals in caring for infertile men?
Our goals include the identification and treatment of reversible conditions that have resulted in infertility, the identification of irreversible causes in which ART using the male partners’ sperm can be performed to produce a pregnancy such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in-vitro fertilization (IVF), the identification of irreversible conditions that required the couple’s use of other options for treatment including donor insemination, the identification of underlying medical problems connected with male infertility, and the identification of chromosomal disorders which might be affecting the male partner or his offspring.
What is a varicocele and how can a varicocele impact a man’s fertility potential?
An abnormal dilation of veins surrounding the testicle is defined a varicocele. Varicoceles are the most common correctable cause of male infertility and are present in 40% of men presenting with infertility. Varicoceles are diagnosed by physical examination. Varicoceles may impair a man’s fertility by impacting the sperm parameters and by causing sperm DNA fragmentation (damage to the sperm’s DNA) which may impair the couple’s ability to conceive.
What is it like to undergo a varicocele repair?
The varicocele is corrected through a one inch incision made in the groin in an area where no major strength layers have to be opened to make the recovery as quick and easy as possible. This is a day surgery and the patient may return to desk work in 1 – 2 days, and usually to full activity in 7 days.
What are the odds of having improved sperm parameters after a varicocele repair?
70% of men who undergo varicocele repair with infertility, abnormal sperm counts, or abnormal sperm function will improve sperm counts/function. Dr. Kavoussi has specialty fellowship microsurgical training for varicocele repair.
What happens if a man chooses to have the varicocele observed rather than repaired?
Not treating a varicocele may result in testicular shrinkage (atrophy) and/or a worsening of semen quality which may lead to infertility. Overtime, the persistent varicocele may lead to permanent, irreversible testicular injury.
How long will it take to see improvement in semen parameters after a varicocele repair?
It will typically take at least 3-4 months to see any improvement in the semen parameters after a varicocele is repaired. Improvement is usually seen within 6 months of varicocele repair, but it may take up to a year to see any change in semen parameters.
Schedule a Private Evaluation with our Austin Male Infertility Expert today! Call (512) 444-1414 or request an appointment online.



